Understanding Decimals
Decimals represent fractions of a whole. In mathematics, a decimal point separates the whole number part from the fractional part. For example, in the number 3.5, ‘3’ is the whole number part and ‘.5’ is the fractional part, representing half.
Importance of Decimals in Baseball Statistics
In baseball, decimals are crucial for measuring player performance. Statistics like batting average and earned run average (ERA) are all expressed in decimal form. These decimals provide a more precise and detailed view of a player’s skills and performance.
Calculating Decimals with Baseball Stats
- Batting Average: This is calculated by dividing the number of hits by the number of at-bats. For instance, if a player has 50 hits in 200 at-bats, their batting average is calculated as:
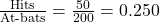
- Earned Run Average (ERA): This is the average number of earned runs a pitcher allows per nine innings. For example, if a pitcher has allowed 40 earned runs over 150 innings, the ERA is:
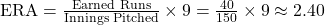
Converting Decimals to Percentages
To convert a decimal to a percentage, simply multiply the decimal by 100 and add the percentage sign. For example:
- If a player’s batting average is 0.300, as a percentage, it’s
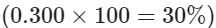 . However in Baseball, no one represents a batting average as a percentage. It’s just important to know that they are two sides of the same coin. A decimal is just a percentage divided by 100. A percentage is just a decimal multiplies by 100
. However in Baseball, no one represents a batting average as a percentage. It’s just important to know that they are two sides of the same coin. A decimal is just a percentage divided by 100. A percentage is just a decimal multiplies by 100 - An ERA of 2.40 is equivalent to
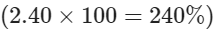 when expressed as a percentage, though ERA is traditionally kept in decimal form.
when expressed as a percentage, though ERA is traditionally kept in decimal form.
Conclusion
Decimals offer a precise way to measure and compare performances in baseball. In terms of what you need to know about decimals, the main takeaway for now is the relationship between decimals and percentages. Later on in the course, we’ll cover decimal odds which is a similar concept but slightly more in depth.
